readme.md 6.7 KB
Solutions of autochecker for chinese
How to use :
1. Make a detecter
- Construct a dict to detect the misspelled chinese phrase,key is the chinese phrase, value is its corresponding frequency appeared in corpus.
- You can finish this step by collecting corpus from the internet, or you can choose a more easy way, load some dicts already created by others. Here we choose the second way, construct the dict from file.
The detecter works in this way: for any phrase not appeared in this dict, the detecter will detect it as a mis-spelled phrase.
def construct_dict( file_path ): word_freq = {} with open(file_path, "r") as f: for line in f: info = line.split() word = info[0] frequency = info[1] word_freq[word] = frequency return word_freqFILE_PATH = "./token_freq_pos%40350k_jieba.txt" phrase_freq = construct_dict( FILE_PATH )print( type(phrase_freq) ) print( len(phrase_freq) )349045
- Make an autocorrecter for the misspelled phrase, we use the edit distance to make a correct-candidate list for the mis-spelled phrase
We sort the correct-candidate list according to the likelyhood of being the correct phrase, based on the following rules:
- If the candidate's pinyin matches exactly with misspelled phrase's pinyin, we put the candidate in first order, which means they are the most likely phrase to be selected.
- Else if candidate first word's pinyin matches with misspelled phrase's first word's pinyin, we put the candidate in second order.
Otherwise, we put the candidate in third order.
import pinyin# list for chinese words # read from the words.dic def load_cn_words_dict( file_path ): cn_words_dict = "" with open(file_path, "r") as f: for word in f: cn_words_dict += word.strip().decode("utf-8") return cn_words_dict# function calculate the edite distance from the chinese phrase def edits1(phrase, cn_words_dict): "All edits that are one edit away from `phrase`." phrase = phrase.decode("utf-8") splits = [(phrase[:i], phrase[i:]) for i in range(len(phrase) + 1)] deletes = [L + R[1:] for L, R in splits if R] transposes = [L + R[1] + R[0] + R[2:] for L, R in splits if len(R)>1] replaces = [L + c + R[1:] for L, R in splits if R for c in cn_words_dict] inserts = [L + c + R for L, R in splits for c in cn_words_dict] return set(deletes + transposes + replaces + inserts)# return the phrease exist in phrase_freq def known(phrases): return set(phrase for phrase in phrases if phrase.encode("utf-8") in phrase_freq)# get the candidates phrase of the error phrase # we sort the candidates phrase's importance according to their pinyin # if the candidate phrase's pinyin exactly matches with the error phrase, we put them into first order # if the candidate phrase's first word pinyin matches with the error phrase first word, we put them into second order # else we put candidate phrase into the third order def get_candidates( error_phrase ): candidates_1st_order = [] candidates_2nd_order = [] candidates_3nd_order = [] error_pinyin = pinyin.get(error_phrase, format="strip", delimiter="/").encode("utf-8") cn_words_dict = load_cn_words_dict( "./cn_dict.txt" ) candidate_phrases = list( known(edits1(error_phrase, cn_words_dict)) ) for candidate_phrase in candidate_phrases: candidate_pinyin = pinyin.get(candidate_phrase, format="strip", delimiter="/").encode("utf-8") if candidate_pinyin == error_pinyin: candidates_1st_order.append(candidate_phrase) elif candidate_pinyin.split("/")[0] == error_pinyin.split("/")[0]: candidates_2nd_order.append(candidate_phrase) else: candidates_3nd_order.append(candidate_phrase) return candidates_1st_order, candidates_2nd_order, candidates_3nd_orderdef auto_correct( error_phrase ): c1_order, c2_order, c3_order = get_candidates(error_phrase) # print c1_order, c2_order, c3_order if c1_order: return max(c1_order, key=phrase_freq.get ) elif c2_order: return max(c2_order, key=phrase_freq.get ) else: return max(c3_order, key=phrase_freq.get )# test for the auto_correct error_phrase_1 = "呕涂" # should be "呕吐" error_phrase_2 = "东方之朱" # should be "东方之珠" error_phrase_3 = "沙拢" # should be "沙龙" print error_phrase_1, auto_correct( error_phrase_1 ) print error_phrase_2, auto_correct( error_phrase_2 ) print error_phrase_3, auto_correct( error_phrase_3 )
呕涂 呕吐 东方之朱 东方之珠 沙拢 沙龙
- For any given sentence, use jieba do the segmentation,
- Get segment list after segmentation is done, check if the remain phrase exists in word_freq dict, if not, then it is a misspelled phrase
- Use auto_correct function to correct the misspelled phrase
Output the correct sentence
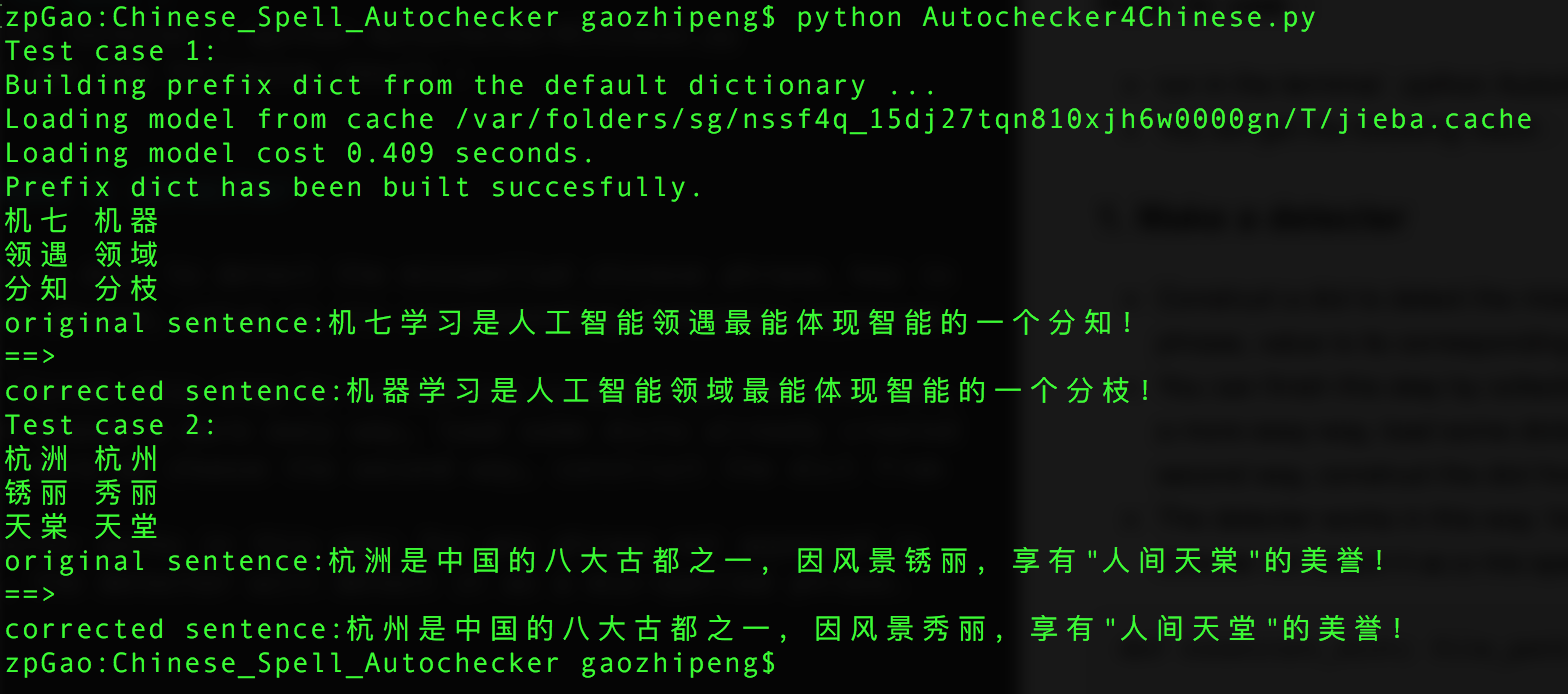
import jieba import string import rePUNCTUATION_LIST = string.punctuation PUNCTUATION_LIST += "。,?:;{}[]‘“”《》/!%……()"def auto_correct_sentence( error_sentence, verbose=True): jieba_cut = jieba.cut(err_test.decode("utf-8"), cut_all=False) seg_list = "\t".join(jieba_cut).split("\t") correct_sentence = "" for phrase in seg_list: correct_phrase = phrase # check if item is a punctuation if phrase not in PUNCTUATION_LIST.decode("utf-8"): # check if the phrase in our dict, if not then it is a misspelled phrase if phrase.encode("utf-8") not in phrase_freq.keys(): correct_phrase = auto_correct(phrase.encode("utf-8")) if verbose : print phrase, correct_phrase correct_sentence += correct_phrase if verbose: print correct_sentence return correct_sentenceerr_sent = '机七学习是人工智能领遇最能体现智能的一个分知!' correct_sent = auto_correct_sentence( err_sent )机七 机器 领遇 领域 分知 分枝 机器学习是人工智能领域最能体现智能的一个分枝!
print correct_sent机器学习是人工智能领域最能体现智能的一个分枝!